raudsters are becoming smarter and fraud rings more sophisticated in financial services, making it harder to detect and prevent fraud.
Bad actors also often coordinate their efforts and conduct seemingly normal transactions across different regions to minimize the risk of exposure. With all these complexities, humans just aren’t capable of quickly identifying suspicious behavior or transactions that are buried in millions of other legitimate transactions.
This is where AI comes in handy. In the case of fraud detection, an AI model is trained on large amounts of historical data—both customer and transactional—to recognize suspicious behaviors and patterns. The first benefit of using AI for this purpose is that the process becomes much quicker.
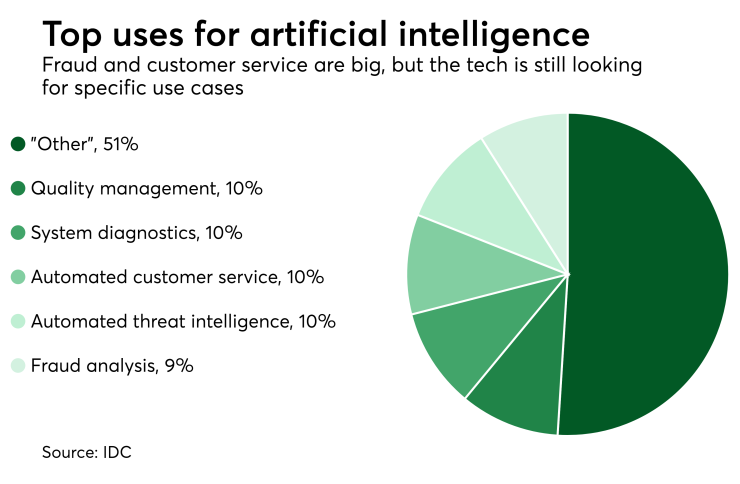
After an AI system is trained to identify irregular events, it can quickly assess new transactions by comparing them with known patterns and spot the smallest anomalies, so humans don’t need to sink hours into processing and analyzing millions of transactions.
A second major benefit is improved accuracy by significantly reducing false positives and false negatives. A well-designed AI system is constantly refined through ongoing model training with fresh data and new classifications, so it becomes smarter over time. As a result, AI does an exponentially better job of correctly identifying abnormal behavior than any human could, and it therefore helps financial services organizations reduce risk and costs, all while enhancing customer satisfaction.
Fraud and automation do indirectly result in a better customer experience—faster application approval, less frequent false positives or false negatives—but AI can also be used to deliver a more personalized experience to customers in other ways.
Omnichannel experience is one of the top priorities for all financial firms. In order to deliver a consistent, seamless customer experience across all channels—direct or digital—a financial organization can leverage machine learning to facilitate a holistic approach.
For example, for a retail bank that offers its services through both brick & mortar and online channels across various business units, AI can quickly act on the consolidated customer data from the bank’s internal and external systems with personalized service and recommendations, and ensure a seamless customer experience across all business channels.





